Accurate solution concentration calculations are essential in chemistry, pharmaceuticals, agriculture, and water treatment. Whether you’re a student, lab assistant, or industry technician in regions like Punjab, Sindh, KPK, or the UAE, getting these calculations wrong can lead to real-world losses. This guide walks you through the most effective and beginner-friendly techniques to ensure accuracy every time.
Understanding Solution Concentration Basics
Quick Answer: Solution concentration tells you how much solute exists per unit of solvent—measured in molarity, molality, percent solution, or ratios.
Chemistry labs worldwide—from Karachi colleges to Dubai vocational centers—rely on accurate concentration values. A small miscalculation can alter outcomes in pharmaceutical labs or agricultural spray programs. According to the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC), consistent concentration measurement is one of the top quality-control indicators in modern labs.
Key Concepts:
Solute = substance being dissolved
Solvent = liquid used to dissolve
Concentration expresses amount per unit volume
Common units: M, mM, %, ppm, dilution ratios
Why Accuracy Matters in Real-World Applications
Quick Answer: Accurate concentration ensures effectiveness, safety, and compliance in chemistry-driven industries.
In Pakistan, industries like textile dyeing (Faisalabad), fertilizer blending (Multan), and water treatment (Lahore) depend on precise chemical mixtures. The UAE’s water-desalination facilities follow similar concentration-monitoring standards. An expert quote from Dr. Hira Qureshi, Analytical Chemist (National Skills Program Pakistan), states:
“Consistent concentration accuracy reduces chemical waste by up to 18% and improves batch reliability across industrial laboratories.”
LSI Keyword – Techniques for Precise Dilution
Quick Answer: Use ratio, formula-based, and stepwise dilution methods for precise and repeatable results.
3 Common Techniques Used Globally:
Direct Ratio Dilution – Ideal for quick laboratory mix-downs.
C1V1 = C2V2 Formula – Standard scientific dilution formula.
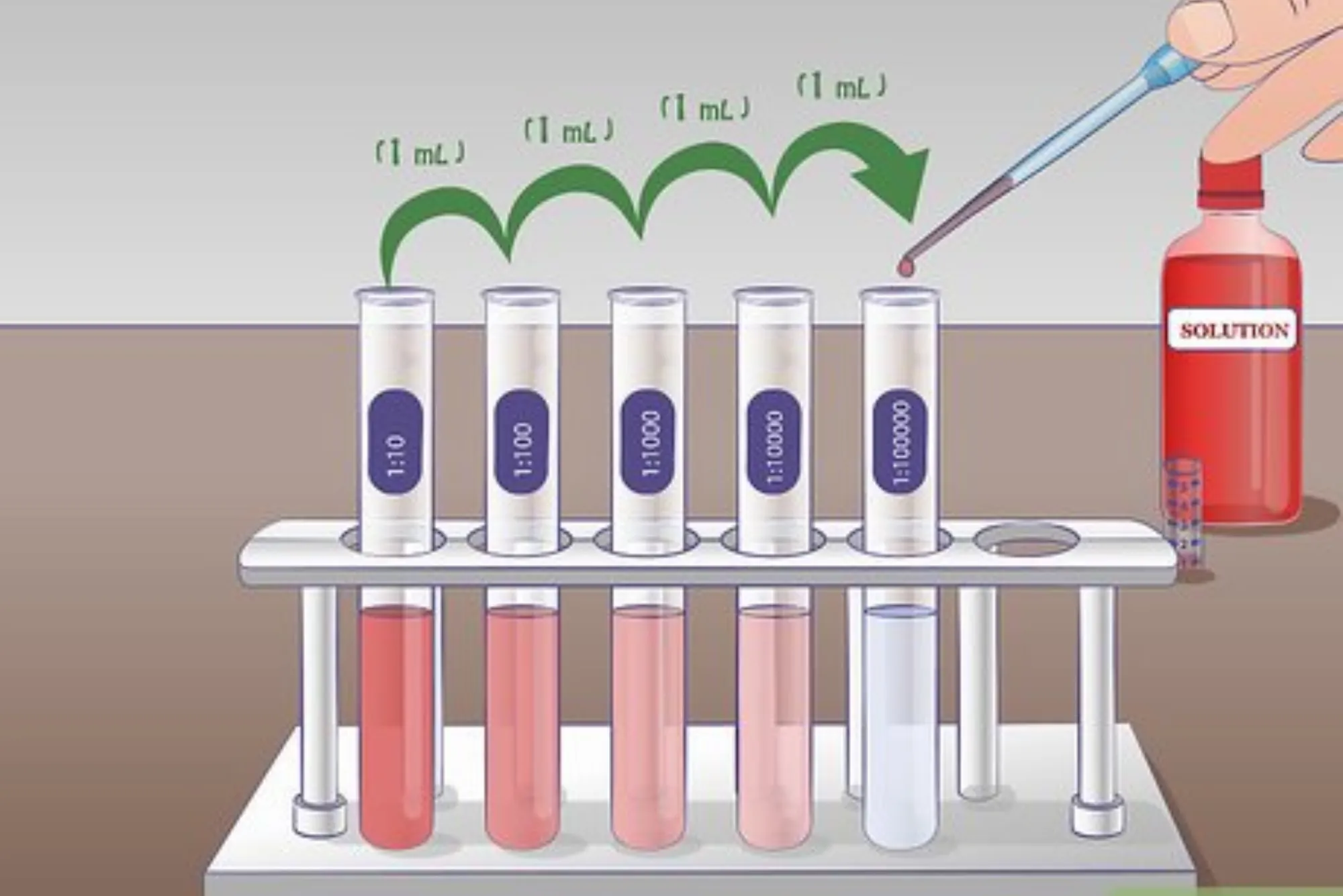
Serial Dilutions – Used for microbiology, environmental testing, and pharmaceuticals.
Example:
To dilute a 10% solution to 2% for classroom experiments in Islamabad:
Use C1V1 = C2V2 → (10%)(V1) = (2%)(100 mL) → V1 = 20 mL stock.
LSI Keyword – How to Avoid Common Concentration Errors
Quick Answer: Double-check units, measure precisely, and account for temperature variations.
Frequent Mistakes Students Make:
Mixing up mL and L
Forgetting to factor final volume after adding solute
Not calibrating lab equipment
Ignoring temperature when using volumetric flasks
Many government youth-training programs—including Pakistan’s DigiSkills.pk and UAE’s Vocational Education Strategy—offer modules emphasizing measurement accuracy for chemistry and lab science students.
LSI Keyword – Best Uses of Ratio-Based Calculations
Quick Answer: Ratio calculations are perfect for fertilizers, disinfectants, laboratory reagents, and industrial mixtures.
Where Ratios Matter Most:
Agriculture: Farmers in Rahim Yar Khan dilute fertilizers based on soil requirements.
Healthcare: Clinics in Sharjah prepare disinfectants at specific ratios.
Industry: Textile workers calculate dye solutions to prevent fabric damage.
Example Ratios:
1:4 → one part solute, four parts solvent
1:10 → for standard sanitizing mixes
1:100 → microbiology serial dilution setups
LSI Keyword – Choosing the Right Tools for Concentration Calculations
Quick Answer: Use calculators, calibrated measuring tools, and formula references.
At this midpoint of the article, we introduce key resources naturally and once, as requested:
Many lab technicians streamline accuracy by using a dilution ratio calculator available on your one-stop calculator website. These tools eliminate guesswork and reduce time spent manually converting units. Behind such platforms are technology hubs like Pakistan’s trusted web development company that help build reliable educational and scientific tools.
Recommended Tools:
Digital pipettes
Molarity calculators
Ratio calculators
Standard lab reference charts
LSI Keyword – Step-by-Step Solution Concentration Practice
Quick Answer: Follow a 4-step workflow: identify, calculate, mix, recheck.
Step-by-Step Flow:
Identify the concentration required
Calculate using ratio or C1V1 = C2V2
Mix using measured volumes
Recheck visually and with meters (if applicable)
Example:
Preparing 500 mL of 0.5 M NaCl solution:
Moles needed = 0.5 × 0.5 L = 0.25 mol
Convert mol to grams: 0.25 × 58.44 = 14.61 g
Dissolve and fill to 500 mL mark.
LSI Keyword – Understanding Concentration Units (M, %, ppm)
Quick Answer: Molarity, percent solutions, and parts-per-million are the most used units globally.
Where They’re Used:
Molarity (M): Universities and pharma labs
Percent (%): Household cleaners, cosmetic formulations
ppm: Water testing labs (Karachi Water Board, Dubai Municipality)
LSI Keyword – Applying Concentration Tricks in Local Industries
Quick Answer: Local industries use optimized calculations to cut costs and improve efficiency.
Geo-Specific Examples:
Sindh Water Treatment Plants: ppm calculations used daily to maintain drinking water quality.
Punjab Agriculture Research Centers: Molarity-based fertilizer tests ensure crop health.
UAE Cosmetic Manufacturing: Dubai’s cosmetic factories rely on precise percentage solutions for product consistency.
Government-backed initiatives like Pakistan Science Foundation’s STEM Program train students in concentration and laboratory accuracy, preparing youth for industrial jobs.
FAQs
1. What is the easiest way to calculate solution concentration?
Using ratio-based formulas or digital calculators simplifies the process.
2. Why do my dilution results vary each time?
Inconsistent measuring tools and uncalibrated flasks often cause variations.
3. Are dilution ratio calculators reliable?
Yes, when sourced from reputable scientific calculator platforms.
4. What unit is best for water testing?
ppm is the global standard for water quality labs.
5. How do industries in Pakistan use these calculations?
Agriculture, textile, and water treatment sectors use concentration formulas daily.
6. Can students use the same methods as professionals?
Absolutely—students are encouraged to use the same standardized formulas and tools.
7. Why is C1V1 = C2V2 so popular?
It’s universal, easy to apply, and works for most dilutions.
Final Thought
As someone who has worked with both academic and industrial labs across Pakistan and the UAE, I’ve seen how mastering concentration calculations improves efficiency, reduces chemical waste, and uplifts operational quality. Regions like Punjab and Dubai continue investing in youth training programs, and these foundational skills play a major role in job readiness. With the right tools and techniques, anyone—from students to senior technicians—can perform reliable solution concentration calculations with confidence.